Giovanni Belzoni, who discovered the tomb in 1817, was a circus man who originally came to Egypt to market an irrigation pump he had designed in England. The project fell through but he arranged the transportation of the colossal head of Ramses II from the Ramasseum to the British Museum in London.
 |
This is a classical tomb that far surpasses all others
in the Valley of the Kings both in size and
in the artistic execution of the sculptured walls.
Every inch of wall space of its entire 100 meter length
is covered with representations which were carried
out by the finest craftsmen. |
He turned his energies to the
Valley of the Kings and made this remarkable find just one year later. When the Turkish officials in Egypt heard of the discovery they straightway made for the tomb, bent on the delightful thought of acquiring priceless treasure. Down the corridors they went, ran sacking every corner only to find to their disappointment that the tomb contained no more than an empty sarcophagus.A steep flight of stairs leads to the entrance of Seti's tomb which is covered with sacred texts along its full length from the highest reaches down to the bed rock. The first corridor (I) is carved in high relief. On the left-hand wall (a) the sun-disc bearing a scarab, and the ram-headed Sun
God can be seen between a serpent , acrocodile and two cows' heads. The texts which start on the left are continued to the right (b). The roof is painted with flying vultures.

The second corridor (2), which is staircased, has thirty-seven forms of the Sun
God depicted on the upper part of the recesses on both sides. As we descend to the third corridor , Maat,
goddess of truth, faces us with outstretched wings above the doorway (r). Isis is represented on the left-hand side (d), and Nephthys (Nebethet) on the right (e), and they both kneel on the hieroglyph for 'gold' and place their hands upon a seal ring. Above them, on each side of the corridor, the jackal-
god Anubis can be seen. The wall reliefs here have not been completed but we can see the outlines in black, the master's touch in red, and the accuracy with which the relief is carved from the bottom up wards.

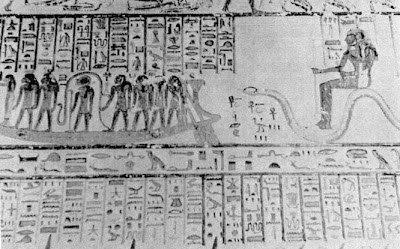
Proceeding beneath Maat with her outstretched wings we pass into the third corridor (3), which has dramatic representations of the fifth hour of night from the fifth chapter of the
Book of the Dead. Towards the middle of the left-hand wall (f) the sun-boat (damaged) is driven through the netherworld by seven
gods and seven
goddesses and in front of it march four
gods and the
goddess Isis. On the right-hand wall (g) the Sun
God and his retinue are drawn through a land inhabited by demons and monsters (top and bottom rows) and we see a serpent with three heads, wings and human legs. But the Sun
God is safe, drawn by Horus and Thoth (middle row) who carry an eye as a protection against evil. The ceiling is blackened from the candles of the early Christians who hid in the tomb, as it is believed.

From the third corridor onwards the quality of the color on the reliefs is superb. We now come to a small ante-chamber (4). The walls, both to left and right, show the Pharaoh between Harmachis and Isis offering wine to Hathor. We now enter a square chamber with four pillars (s) . On the pillars themselves the Pharaoh is shown before the various deities: Isis and Nephthys (Nebethet) the sister-wife and the sister of Osiris, Harbor the
goddess of joy and love who was also the
goddess of Dendera to whom the cow was sacred, Selket the
goddess to whom the scorpion was sacred, Horus the universal Sun
God, and Harsiesis and Harmaches who were special forms of Horus; also of course Anubis, the jackal-
god of embalming. The walls, especially those at the sides, have marvelous representations of the sun travelling through the fourth region of the underworld. On the rear wall (h) Osiris is enthroned before Hathor while the Pharaoh is led into his presence by the hawk-headed Horus. This is a superb mural with intricate detail and rich color. Near the corner of the left-handwall (i) the four chief races of men known at the time stand before Horus: these are Egyptians, Asiatics with pointed beards and colored aprons, four backs and four Libyans with feathers on their heads and tattooed bodies.The chamber (6), situated to the right and entered via an arrow flight of steps, was never completed. Whether this was because it was discovered that the walls were of inferior material, or as a blind to mislead grave-robbers, is not known, but the sketches on the walls are bold and compelling and show the touch of a master craftsman. The original sketch was done in red. The corrections in black were probably the work of the senior artist , after which the carvers took over. The left-hand wall (j) shows the journey during the ninth hour of the underworld: the sacred cow, ram, bird and human head guarding the procession against the fiery serpents. On the rear-wall (k) is the tenth hour with the hawk joining the protective deities and the spirits carrying arrows and lances. On the right-hand wall (I) is the eleventh hour with the condemned in the
lower row. The enemies of the Sun
God are being burned under the supervision of the hawk-headed Horus in strange furnaces, whilst fire-breathing
goddesses stand watch with swords.
We retrace our steps to the chamber of pillars (s), to the left of which a stairway, carefully concealed by the builders of the tomb, descends to the fourth corridor (7). To the left of this corridor (m) is a figure of the Pharaoh (destroyed) seated at an offering table. Above him hovers a hawk and before him stands a priest.
We descend a few more steps into a small corridor (8) which is decorated with texts of the ceremonies performed before the statue of the deceased Pharaoh in order that he may eat and drink in the hereafter. On the right-hand wall (n) is a list of offerings.
 |
The picture above is of an unfinished relief work at the tomb of Seti I |
 |
The picture above is for a scene from burial chamber of Seti I's tomb |
The ante-chamber (9) is decorated with the
gods of the dead including Anubis, Isis, Hathor, Harsiesis and Osiris. Finally we come to a large hall (10). Here a slight incline with steps at the sides takes us to the mummy-shaft, which comprises two portions. The front portion has pillars and the rear portion a vaulted ceiling. It was in the front section that the alabaster sarcophagus of the Pharaoh stood when
the tomb was discovered. It was made out of a single piece of alabaster, carved to a thickness of two inches and with the exquisite reliefs filled in with blue paste. This magnificent piece is comparable only to the alabaster vase found in
Tutankhamun's tomb which is today in the Cairo Museum. The mummy, which was one of those found at
Deir el Bahri (Hatshepsut's Temple), is in the same museum. The sarcophagus lies in the Soane Museumin in London. When Belzoni, who was commissioned to transport it, took it to the British Museum, the trustees considered the price set too high and the treasure was without a buyer until 1824 when Sir John Soane paid £2,000 for it. The decorations on the walls of the pillared portion of the hall show the journey through the first region of the underworld on the left entrance-wall (0) and through the fourth region of the underworld on the left-hand wall (p). In a small recess at the end of this wall (q) is a beautiful representation of Anubis performing theopening-of- the-mouth ceremony before Osiris. On the right-hand entrance wall (r) and the right-hand wall (s) are representations of the journey through the second region of the underworld. The vaulted ceiling has been painted with astrological figures. From early times, of course, the Egyptians had mapped out the heavens, identified some of the fixed stars and were able to determine the positions of others. This ceiling is unusual in that it has not been painted in the familiar balanced, repetitive form. Adjoining the tomb chamber are four side-rooms. The first one on the right (11) has the text of a myth that concerns the rebellion of mankind against the Sun
God, their punishment and final rescue. On the rear wall is a magnificent relief of the heavenly cow of the myth supported by Shu, the
god of the atmosphere,and bearing on its back two boats of the sun.
The chamber on the left (12) has a shelf decorated with a cornice running around the three main walls. It contains more dramatic representations of the Pharaoh's progress through various provinces, safeguarded by the spells of Isis, the sacred Ibis and the ostrich feather - symbol of justice and truth. Spirits and demons (left-hand wall (t), middle row) greet the procession. The foes of Osiris are beheaded by a lion-headed
god (top row), and dwellings of the deceased
gods and spirits open their doors as the Sun
God approaches (rear wall (u), middle row), showing the dead restored to life, and serpents with heads of genii of the dead upon their backs, or with swords in their hands, rising in unison to annihilate the foes of the Sun
God at the end of the journey.
The Pharaoh will overcome. With the help of the Sun
God the doors of the hereafter are open to him. He will enter with his valuables and possessions; with the ability to eat and drink; and imbued with life so as to reign again. This is his ultimate hope.
 The roof of the second corridor (2) is decorated with constellations. To both left and right (e) serpents rear themselves. Note the recesses for figures of the gods, followed on the left-hand wall (f) with the beginning of another text from the Book of the Dead and the deceased Pharaoh before the hawk-headed Sun God . On the opposite wall (g) are demons and spirits.
The roof of the second corridor (2) is decorated with constellations. To both left and right (e) serpents rear themselves. Note the recesses for figures of the gods, followed on the left-hand wall (f) with the beginning of another text from the Book of the Dead and the deceased Pharaoh before the hawk-headed Sun God . On the opposite wall (g) are demons and spirits. The third corridor (3) is also protected by serpents. On the right-hand wall (h) the Pharaoh presents an image of Maat to Ptah, the god of Memphis, beside whom stands the goddess Maat. Note that the transparent cloth of the skirt is cut in low relief thus enabling the foot and front legs of the Pharaoh to appear in high relief. Immediately beyond this representation we see the mummy of the Pharaoh across a mountain, symbolizing the resurrection.
The third corridor (3) is also protected by serpents. On the right-hand wall (h) the Pharaoh presents an image of Maat to Ptah, the god of Memphis, beside whom stands the goddess Maat. Note that the transparent cloth of the skirt is cut in low relief thus enabling the foot and front legs of the Pharaoh to appear in high relief. Immediately beyond this representation we see the mummy of the Pharaoh across a mountain, symbolizing the resurrection. The scarab and the sun-disc (above) indicate the bringing forth of renewed life on the earth. Towards the middle of this same wall (at i) are ritualistic representations including four men spitting out scarabs as they bend over backwards, demons standing upon serpents, serpents pierced by arrows and the scarab in a boat with two Horus eyes.
The scarab and the sun-disc (above) indicate the bringing forth of renewed life on the earth. Towards the middle of this same wall (at i) are ritualistic representations including four men spitting out scarabs as they bend over backwards, demons standing upon serpents, serpents pierced by arrows and the scarab in a boat with two Horus eyes.